A Break in The Sagittarius Arm!
Highlights:
1. Break is due to higher angle of Star Formation (SF) region than previously predicted.
2. Found by mapping the radial velocities of stars in the region.
3. The SF region is 44 deg higher than previously predicted giving rise to notion of break in the continuous arm.
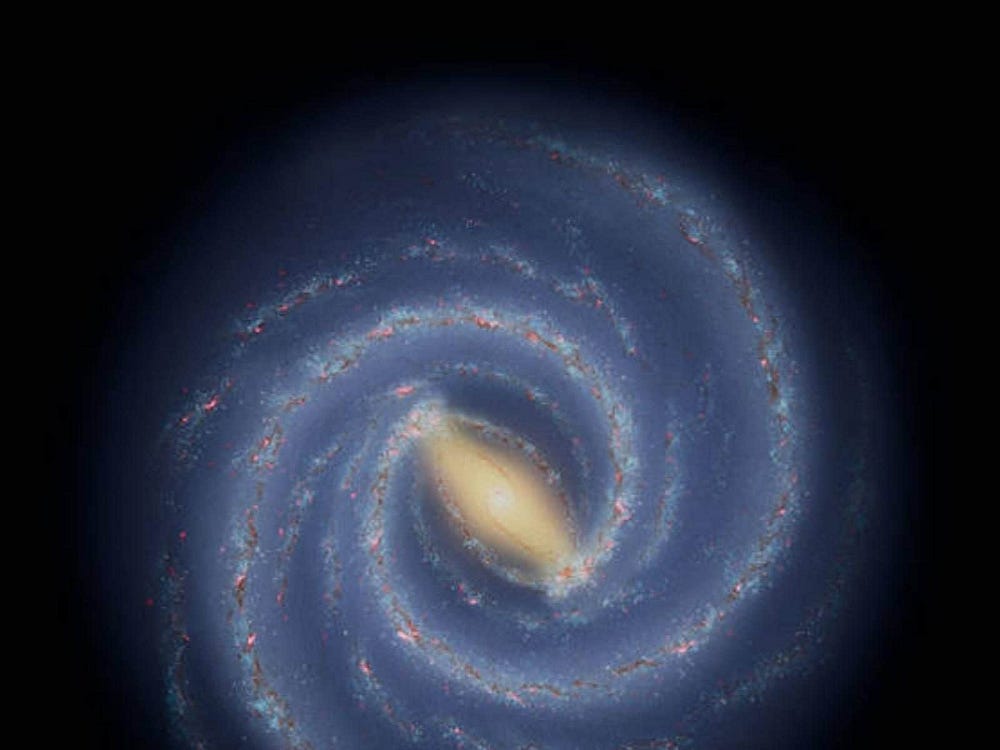

This illustration shows astronomers’ current understanding of the large-scale structure of the Milky Way. Stars and star-forming regions are largely grouped into spiral arms. Measuring the shape, size, and number of spiral arms is a challenge because Earth is located inside the galaxy. Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Living inside the Milky-way Galaxy it is very difficult to observe our own Galaxy. So, most of our understanding of our Galaxy’s structure comes from observation of other Spiral Galaxies. Spiral arms determine how the Star Forming (SF) regions would be. All’ s good here as generally in Spiral Galaxies, SF regions trace the spiral pattern of their respective arms.
What changed suddenly?
While studying the Sagittarius arm of our galaxy(Sun is in the Orion arm), scientists found an unusual break, meaning, they found SF regions at a higher angle than what was previously thought. (Refer to Fig below)
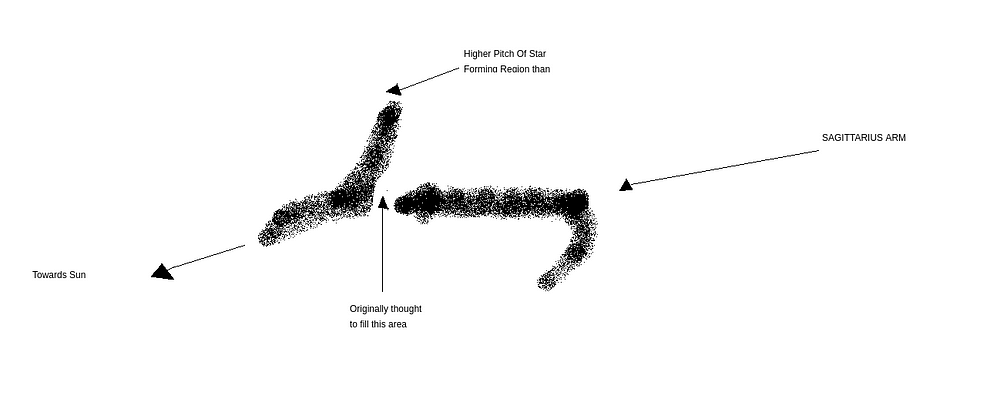
Illustration of Break (Not an actual representation, just for understanding higher pitch angle and helping in visualization.)
This meant that, in the Sagittarius arm, SF regions didn’t trace the general spiral pattern as was previously thought. This was unremarkable for the general model of the Spiral Galaxies.
How did Scientists find out about the break?
For this, they traced groups of Young Stellar objects (YSO), which are a link between stellar content and spiral arms. Mapping the radial velocities of stars in the YSO they found a pattern that was never observed before.
Measuring their radial velocities and plotting it against Galactic longitude, they found the unusual break in the arm.
For this, they used data from Spitzer/IARC telescopes and the data from the Gaia telescope was used for measuring distances. One Reason for using YSO groups was that the parallaxes are more easily determined for a group of objects. To be sure and to eliminate any unwanted errors, they used 8 groups of YSO.
Thus, such discoveries are beacons that a lot more is unknown about our own galaxies, let alone other nearby Galaxies or the Observable Universe.
The paper was published in Astronomy & Astrophysics Journal on 21 July 2021.
Comments
Post a Comment